References:
Referent: prof. Domenico Luca Carnì
Body: University of Calabria – Department of Computer Engineering, Modeling, Electronics and Systems
seat: via P. Bucci, Cube 41C floor 6
Contacts
- Tel: 0984 494240 (Prof. Meat)
- Tel: 0984 49 2375 (Green HoMe)
- Web: www.greenhomescarl.it/laboratorioknx
Lo standard KNX
bus technology KNX (already identified as Konnex) it is an open world standard, for the realization of home and building automation applications: lighting, warm up, ventilation, air conditioning, shading, security systems, monitoring, alarms, energy management, measurement, domestic appliances, audio/video, etc.
KNX was born over the years 90 in Europe and today counts more than 450 members and 80.000 certified operators (system integrator KNX) in the world.
KNX has been approved as standard European (IN 50090 - IN 13321-1), Chinese (GB / T 20965) and worldwide (ISO/IEC 14543) (rif. standard KNX )
Among the advantages of the KNX system there is the verification of conformity of the products labeled with the KNX mark which they therefore guarantee, in addition to the support of the KNX protocol, data standardization and full compatibility between devices from different manufacturers.
The programming and implementation of KNX systems is based on a single programming tool which is called ETS, currently come to version 5.6. (about ETS software)
With the introduction and development of Web Services, the KNX Standard can be integrated with the other main building automation standards (quali BACnet, DALI, ModBus, Lonworks, Enocean, ecc.) and also within the various BMS systems (Building Management System) for management, the control and maintenance of buildings and related processes.
KNX can be used with different means of communication: cavo twisted, radio frequency, power line and ethernet / WiFi cable. E’ a further evolution is underway that will lead to the KNX IoT format while the KNX Secure mode is already available, which offers high security of communication and system-user interaction.
The KNX Laboratory is in the start-up phase as part of the activities of the Green HoMe Innovation Hub.
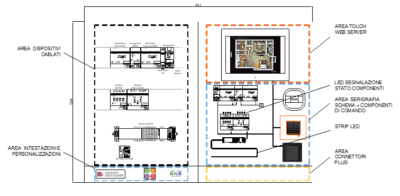
The Laboratory has designed a KNX educational panel on which it is possible to carry out the wiring and configuration operations that would be necessary in a real panel, with the possibility of creating different scenarios in a residential or industrial environment.
The panel includes several functional modules to emulate home and building automation applications:
- IP interface
- Motor power supply actuators
- Single-phase load power supply actuators
- DC load power supply actuators
- Safe connection system for devices
- Command result display system based on web server and touchscreen for greater flexibility in creating different usage scenarios with the same panel and inserting new devices
- Electrical panel with DIN guide on which to install additional home automation components (actuators, couplers, power supplies and / or interfaces)
The KNX Laboratory was started by the Green HoMe Polo in collaboration with the research group of prof. Carnì of DIMES and some associated companies.
The goals of the KNX laboratory are both educational and service to companies and professionals.
The teaching is aimed at business and professional users but also at university level and for professional schools.
The Laboratory carries out dissemination activities (dating, seminars, webinar) and training with introductory courses and courses for KNX certification.
At the university level, the laboratory can provide exercises in degree courses, masters and advanced training courses in which interest is expressed in the field of home automation and electrical systems.
As for the services, the Laboratory provides services of:
- Assistance in planning, configuration, maintenance and use of home automation systems based on KNX modules.
- Characterization of new apparatuses / devices to verify their adherence to the KNX standard.
- Evaluation of the configuration of the modules for the construction of a home automation system based on real application scenarios through the creation of a test bench emulating the one to be installed.
- Tests of software modules made by companies on real and KNX certified components
- Device testing to verify interoperability with KNX modules